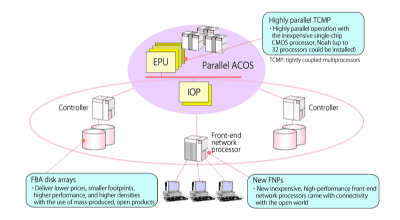
The ACOS-4/XVP PX (which stood for “extended multi virtual processor, parallel extended”) was an operating system intended for NEC’s mid-range and large mainframes. NEC announced the operating system in July 1994 and started shipments in October 1994.
ACOS-4/XVP PX offered connectivity with open systems, realized large cost savings by adopting cutting-edge hardware technologies, and lengthened its advantage over other operating systems through various mainframe architecture revisions, such as parallel processing and cluster technologies. ACOS-4/XVP PX ran on Parallel ACOS mainframe series models, starting with the PX7500, which was announced in July 1994, and followed by the PX7800, PX7600SV, and PX7800SV.
The main features of the operating system and its new architecture are given below.
- 1. Parallel processing
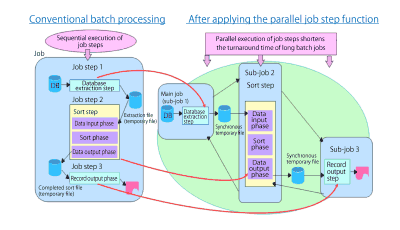
- ACOS-4/XVP PX provided a new information processing platform by adding parallel processes for online transaction processing (OLTP) — important in the service processing area — batch jobs, and database processing.
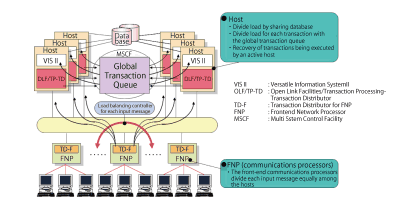
- (1) Division of transaction loads
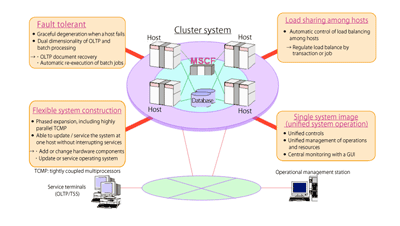
- ACOS-4/XVP PX provided parallel OLTP for cluster systems consisting of multiple hosts. Parallel OLTP raised the system’s overall transaction throughput by allocating and parallel processing transactions among multiple hosts while keeping the load balanced.
- To split transaction loads, parallel OLTP used a load balancing controller, to allocate transactions equally among multiple hosts, and a global transaction queue, a transaction queue that is shared between hosts. Parallel OLTP was also fault tolerant; if a host failed while processing a transaction, the system would recover and re-execute the transaction on another host.