NEC announced the ACOS-2/XP (which stood for “extended processor”) operating system designed for compact mainframes in May 1994 and began shipping the operating system in July.
ACOS-2/XP ran on the compact AX7300 and AX7300V models of the Parallel ACOS mainframe series, which packed all the calculation processing functions into one NOAH chip, a CMOS processor. To address the rise in end-user computing, driven by personal computers and workstations, as well as centralized processing of mission-critical operations, ACOS-2/XP provided a number of software functions making it easier for end-user departments to access data on host computers.
The main features of the operating system are given below.
- 1. Features for parallel processing and higher performance
- ACOS-2/XP provided parallel batch functions as a new parallel processing technology to maximize the performance of shared-memory parallel systems. The operating system also supported functions that harnessed solid-state drives, LAN processors, and other components for high-speed processing of large amounts of data.
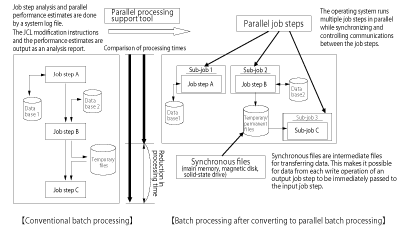
- (1) Parallel batch functions
- Parallel batch functions made it possible to execute multiple job steps within a job in parallel. Parallel batch functions consisted of parallel job steps and synchronous files. By making simple modifications to the job control language (JCL) and no modifications to the application program, it was possible to improve the parallel execution of a job and dramatically raise the batch processing performance. NEC provided analytic tools to help make these JCL modifications.
- (2) Higher performance
- ACOS-2/XP provided a number of functions that allowed performance gains to be made. It supported the use of LAN processors to speed up the processing of the industry standard TCP/IP protocol. It provided automatic save/restore functions to assist the operation side of solid-state drives, which were much more cost effective than other memory devices. And it provided online engine functions that managed transmission messages in main memory and job acceleration functions that preloaded the JCL in main memory.
- 2. Connectivity with open systems
- ACOS-2/XP provided several functions, some of which are given below, to link personal computers used within a corporation and to promote connectivity between mission-critical systems and open systems in the interest, mainly, of using Windows and using mission-critical databases.
- (1) Versatile information system (VIS) / visual environment (VE)
- VIS/VE created a GUI for core operation systems implemented by the VIS and provided data connectivity with open system environments. This allowed seamless operation in Windows environments and the construction of client-server systems in which mission-critical applications running in ACOS-2 and applications running in Windows were linked. ACOS-2/XP had other functions, such as remote file access and remote job entry.
- (2) Open database connectivity (ODBC) support
- ODBC, put forth by Microsoft, was a de facto standard protocol for accessing databases from a Windows environment. ACOS-2/XP, by supplying an ODBC add-on function, linked to an ODBC driver running in Windows and enabled software that supported ODBC to access, via a server, the database RIQS in ACOS-2. This permitted the construction of systems where commercial software that supported ODBC or programs created with commercial development tools could access mission-critical databases.
- 3. Features to improve reliability and operability
- ACOS-2/XP was designed to deliver a higher order of reliability and operability to mission-critical operations on the host computer. This included support to make effective use of disk arrays, uninterruptable power supplies (UPS), and other hardware components as well as the following functions.
- (1) System activity monitoring function
- This function not only graphically represented system activity (CPU utilization rate, number of executing jobs, memory usage, disk I/O information, network message activity); it also quickly detected any declines in response performance. The function was also designed to improve usability as an operator terminal by letting users specify fault alerts, designated message reports, and other selected events.
- (2) Dynamic space management function
- This function reduced the file assignment work associated with service expansion by using multiple volumes for storing work files and other system files and by automatically optimizing file allocations.