NAS-100 was the postal code reading and sorting machine which NEC started to provide in 1997. It supported seven-digit postal codes and adopted the route sequence assembly method which lined up in the mail delivery sequence. The table below gives an overview of the NAS-100.
The primary specifications of the NAS-100 new postal code reading and sorting machine :| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| External dimensions | Main unit: 17,895 x 1,395 x 2,000 mm (w x d x h) Reference: OCR (sorter) units: 800 x 480 x 1,710 mm x 4 frames |
| Weight | 6,800 kg (including the OCR (sorter) units) |
| Actual maximum processing speed | Postal code reading mode: 50,000 mail items per hour (postcards only) Destination address reading mode: 30,000 mail items per hour |
| Mail items handled | Standard size mail items Length: 140 to 235 mm Width: 90 to 120 mm Thickness: 0.2 to 6.0 mm |
| Reading codes | Postal codes (all seven digits) Destination addresses (municipal district, town, district, block, house number, apartment number) |
| Power supply | 200 VAC, three-phase four-line system |
| Power consumption | 34 kVA |
The NAS-100 had several sorting slot configurations: 150-slot, 200-slot, 250-slot, 300-slot, 350-slot, and 400-slot. The specifications given above are for the 400-slot system.
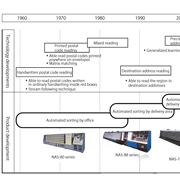
【History of mail sorters】
NEC developed a sorter in 1968, which read the three digits of postal codes and separated mail items into the different slots corresponding tothe destination post offices. In around 1980, the NAS-80 series recognized the postal codes printed on mailing labels and realized to read mail items with handwritten and printed postal codes mixed. In 1989, the NAS-88 series implemented to read addresses of flexible handwritten characters, using multi-stage elasticity comparison technology originally developed by NEC, and address recognition processing together. In 1994, NEC had developed high-precision mail OCR machines using generalized learning vector quantization (GLVQ) and address character tagging technologies in order to read entire postal addresses. These machines could read not only town names and street addresses but also apartment building names and room numbers with high precision detail.
《Notes》
Multi-stage elasticity comparison technology : the individual character recognition technology to adjust expansion and contraction parts using dynamic programming methods, adopting direction characteristics and gradation / displacement shadings of an character.
Generalized learning vector quantization (GLVQ) technology: the NEC original technology to automatically generate character recognition dictionaries (standard patterns) to identify characters and figures.
Address character tagging technology : the address identification technology utilizing character selection candidates and knowledge processing, using a character or left-/ right-hand side part of a character as the fundamental component.