
- Home >
- Artifacts of IP Heritage >
- 2015 >
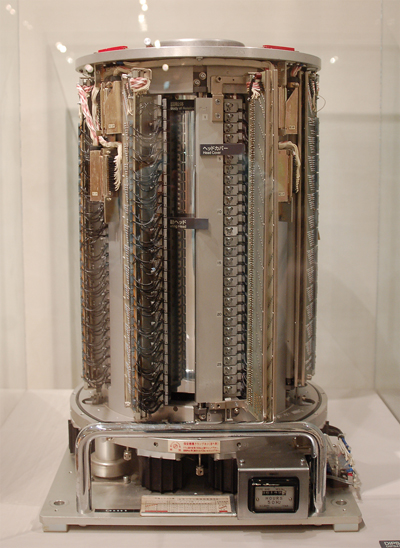
- DIPS4150 magnetic drum units
| Manufactured in | 1969 |
|---|---|
| Manufactured by | Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Public Corporation (now NTT), Hitachi, Ltd. |
| Owner | Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation |
| Location of historical materials | NTT History Center of Technologies NTT Musashino Research and Development Center 3-9-11, Midori-cho, Musashino-shi, Tokyo Japan 180-858 |
| Visitor information | Open to the public |
| Contact | NTT History Center of Technologies Tel.+81-422-259-2093
https://hct.lab.gvm-jp.groupis-ex.ntt/english/contact.html |
The DIPS 4150 magnetic drum units were developed and used for the DIPS-1, which was the information processing system of Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Public Corporation (now NTT) for large scale data communications. The main objective of their development was to realize the data swapping out facilities, achieving the predefined performance in high speed I/O operations.
The DIPS 4150 adopted the "floating" read/write head technology which was the highest level in the world at that time, and achieved 10 times higher density in data recording compared to the "fixed" read/write head model. This magnetic drum memory unit equipped with 823 floating read/write heads had a memory capacity of 4 MB, information recording density of 56 bit/mm, rotation speed of 3000 rpm, average access time of 10.3 ms, and achieved information transfer rate of 2.2 MB/s with the eight parallel track reading and writing.
The magnetic core memories used in DIPS-1 system for main memory units which were extremely expensive and accounted for approx. 30% of the host-center system hardware cost. DIPS 4150 magnetic drum memory units were applied for the data swapping out storage and realized high-capacity, high-speed virtual memory to reduce the system cost.
The first DIPS-1 was installed as the commercial field test-bed system in the Shiba Subscriber Exchange Office of Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Public Corporation in Tokyo, and followed many systems for scientific/engineering computation services (e.g. DEMOS-E) and banking services.
